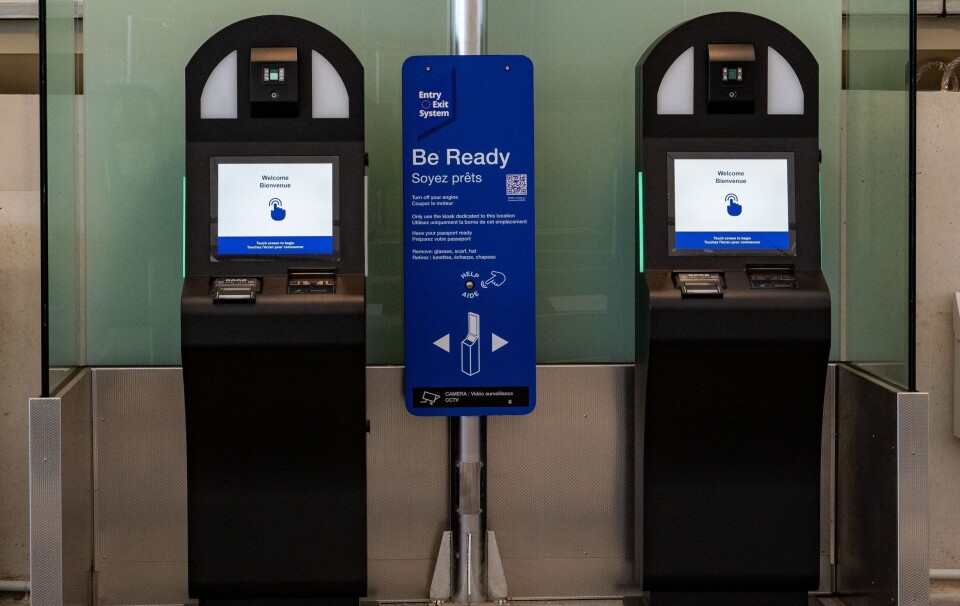
Anyone applying for a multi-year residency permit, resident’s card or for French naturalisation will need to pass a new civic exam (examen civique) from January 2026.
The multiple-choice test, written in French, assesses knowledge of Republican values, institutions, rights and duties, French history and daily life.
To pass, candidates must correctly answer at least 80% of the 40 questions - no more than 8 wrong answers.
The government says there will be three slightly different tests depending on the reason for taking them, however the overall content will be similar.
Below we have compiled our own version of what the civic exam could look like in English taking examples from official government regulations on the contents of the exam.
Part one: Principles and values of the Republic (11 questions)
1. What are the three words of the French national motto?
A. Justice, Equality, Fraternity
B. Liberty, Equality, Fraternity
C. Law, Nation, People
D. Faith, Hope, Charity
Click to show answer
B. Liberty, Equality, Fraternity
2. What does “equality” mean in the French Republic?
A. Everyone should have similar income
B. Everyone has equal rights and duties under the law
C. Men have more rights than women
D. Citizens are equal but foreigners are not
Click to show answer
B. Everyone has equal rights and duties under the law
3. Which of the following is not an official symbol of the Republic?
A. The tricolour flag
B. The cockerel
C. The euro currency
D. The figure of Marianne
Click to show answer
C. The euro currency
4. The national day of France is celebrated on:
A. May 1
B. July 14
C. November 11
D. December 25
Click to show answer
B. July 14
5. What does “laïcité” mean?
A. The rejection of all religions
B. Freedom of conscience and separation of religion and the state
C. Freedom to practise only the Catholic religion
D. The right of teachers to display religious symbols
Click to show answer
B. Freedom of conscience and separation of religion and the state
6. Under the principle of laïcité, can a public official wear visible religious symbols while working?
A. Yes, always
B. Only during religious holidays
C. No, because they must remain neutral
D. Only if their superior agrees
Click to show answer
C. No, because they must remain neutral
7. A parent refuses to have their child take part in a class activity with a teacher who is known to belong to a different religious community. The school insists that the parent must let their child participate. Who is right?
A. The parent, because religion is banned
B. The school, because laïcité protects freedom from discrimination
C. Neither, both must compromise
D. The local mairie
Click to show answer
B. The school, because laïcité protects freedom from discrimination
8. A shopkeeper refuses to serve a woman wearing a headscarf. Is this legal?
A. Yes, because of laïcité
B. No, it is discrimination
C. Yes, if the shopkeeper disagrees with her beliefs
D. Only in public buildings
Click to show answer
B. No, it is discrimination
9. According to the constitution, who holds national sovereignty?
A. The president
B. The government
C. The people
D. Parliament
Click to show answer
C. The people
10. A citizen refuses to pay taxes because they disagree with government policy. Is this acceptable?
A. Yes, it is an act of protest
B. No, paying taxes is a civic duty that funds public services
C. Only if others do the same
D. Only during elections
Click to show answer
B. No, paying taxes is a civic duty that funds public services
11. During a crisis, a citizen volunteers at a food bank. Which republican value does this express most clearly?
A. Freedom
B. Fraternity
C. Equality
D. Neutrality
Click to show answer
B. Fraternity
Part two: Institutions and political systems (6 questions)
12. How is the French president elected?
A. By parliament
B. By citizens through direct universal suffrage
C. By regional assemblies
D. By the constitutional council
Click to show answer
B. By citizens through direct universal suffrage
13. Who makes French laws?
A. The Cour de cassation
B. The president
C. The Assemblée nationale and the Senate
D. The prefects
Click to show answer
C. The Assemblée nationale and the Senate
14. How long is the presidential term in France?
A. 5 years
B. 6 years
C. 7 years
D. 4 years
Click to show answer
A. 5 years
15. Which level of local government is responsible for primary schools?
A. The region
B. The department
C. The commune
D. The state
Click to show answer
C. The commune
16. Which institution ensures that laws comply with the Constitution?
A. The Cour des comptes
B. The Conseil d'État
C. The Conseil constitutionnel
D. The Ministry of Justice
Click to show answer
C. The Conseil constitutionnel
17. Which of the following is an institution of the European Union?
A. The Council of Europe
B. The European Parliament
C. The UN Security Council
D. Nato
Click to show answer
B. The European Parliament
Part three: Rights and duties (11 questions)
18. Which text first declared the rights of citizens in France?
A. The Charter of the environment
B. The Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen (1789)
C. The Napoleonic Code
D. The Maastricht Treaty
Click to show answer
B. The Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen (1789)
19. Which of the following is not a fundamental freedom?
A. Freedom of expression
B. Freedom of marriage
C. Freedom to bear arms
D. Freedom of religion
Click to show answer
C. Freedom to bear arms
20. What is the main role of the police and gendarmerie?
A. To enforce the law and protect the public
B. To decide new laws
C. To collect taxes
D. To manage elections
Click to show answer
A. To enforce the law and protect the public
21. Paying income tax in France is:
A. Optional for new residents
B. A civic obligation that supports public services
C. Voluntary for those under 25
D. Only for French citizens
Click to show answer
B. A civic obligation that supports public services
22. You witness someone vandalising public property. What is the correct civic reaction?
A. Ignore it
B. Film it and post online
C. Inform the police
D. Confront the person violently
Click to show answer
C. Inform the police
23. Your neighbour plays loud music late at night every day. Which principle applies?
A. Freedom of expression
B. Respect for public order and others’ rights
C. Right to culture
D. Freedom of creation
Click to show answer
B. Respect for public order and others’ rights
24. What document guarantees the independence of the judiciary?
A. The Penal Code
B. The Constitution
C. A prefect’s decree
D. The Civil Code
Click to show answer
B. The Constitution
25. Who can be a juror in a criminal trial?
A. Any French citizen over the age of 23 with full civic rights
B. Only lawyers
C. Police officers
D. All adult residents
Click to show answer
A. Any French citizen over the age of 23 with full civic rights
26. You are stopped by the gendarmerie for a road check. What should you do?
A. Drive away quickly
B. Refuse to show documents
C. Comply calmly and show requested papers
D. Argue that it is illegal
Click to show answer
C. Comply calmly and show requested papers
27. The right to strike is protected by:
A. The labour code and the Constitution
B. The Code civil
C. Municipal rules
D. Employer agreements
Click to show answer
A. The labour code and the Constitution
28. Civic solidarity between generations is shown through:
A. The retirement system
B. Traffic rules
C. Religious holidays
D. Marriage laws
Click to show answer
A. The retirement system
Part four: History, geography and culture (8 questions)
29. The French Revolution began in:
A. 1776
B. 1789
C. 1804
D. 1848
Click to show answer
B. 1789
30. Who made the famous appeal of 18 June 1940 from London?
A. François Mitterrand
B. Charles de Gaulle
C. Napoleon Bonaparte
D. Jean Moulin
Click to show answer
B. Charles de Gaulle
31. When was the death penalty abolished in France?
A. 1977
B. 1981
C. 1992
D. 2000
Click to show answer
B. 1981
32. Metropolitan France shares a land border with how many countries?
A. 4
B. 6
C. 8
D. 10
Click to show answer
C. 8
33. Which of the following is an overseas department?
A. Corsica
B. Guadeloupe
C. Andorra
D. Luxembourg
Click to show answer
B. Guadeloupe
34. Approximately how many people live in France in 2025?
A. 50 million
B. 58 million
C. 68 million
D. 80 million
Click to show answer
C. 68 million
35. Which monument is associated with the French Revolution?
A. Eiffel tower
B. Bastille prison
C. Mont Saint-Michel
D. Versailles
Click to show answer
B. Bastille prison
36. The international organisation that promotes the French language is called:
A. Unesco
B. Organisation internationale de la Francophonie
C. OECD
D. Nato
Click to show answer
B. Organisation internationale de la Francophonie
Part five: Living in French society (4 questions)
37. Which of the following is an essential administrative duty after moving to a new address?
A. Attending a welcome day for new arrivals at the mairie
B. Declaring the new address to the authorities
C. Applying for asylum
D. Registering to vote
Click to show answer
B. Declaring the new address to the authorities
38. Who should you see first for most non-emergency medical issues?
A. The hospital
B. Your GP (médecin traitant)
C. The prefecture
D. The mayor
Click to show answer
B. Your GP (médecin traitant)
39. The standard legal working week in France is:
A. 35 hours
B. 37 hours
C. 40 hours
D. 45 hours
Click to show answer
A. 35 hours
40. For what ages is schooling compulsory in France?
A. 3 to 16 years old
B. 6 to 18
C. 5 to 17
D. 7 to 14
Click to show answer
A. 3 to 16 years old